GIS Map Gallery Geographic Information System
|
 |
Lc/Ls – glaciolacustrine sand, silt, and clay
Glaciolacustrine sediments were deposited in proglacial lakes which formed just beyond the front margin of the glacier. Lake Agassiz was the largest proglacial lake in Manitoba. Image 26 depicts rhythmically bedded clay and silt (Unit Lc) overlying glacial till. Lake Agassiz was an extremely large lake, which generated considerable wave energy that eroded headlands and deposited shoreline features composed of sand and gravel in more sheltered areas (Unit Ls). Image 27 is a computer-generated image of a small island rimmed by a beach ridge. Unit Lc represents sediments deposited in the deep water of Lake Agassiz. In places, these sediments (glaciolacustrine clay) draped pre-existing landforms still apparent on the surface today where the sediment is thin (Image 28). Because the north shore of the lake was commonly glacial ice, many icebergs floated in the lake. Where the water was shallow enough, icebergs scoured the floor of the lake (Image 29). Selenite rosettes (crystallized gypsum) are commonly found in Unit Lc (Image 30).
 Image 26
|
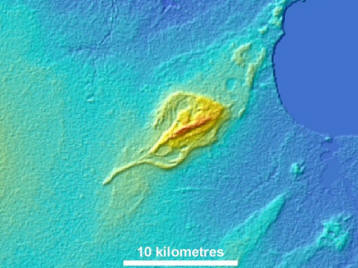 Image 27 |
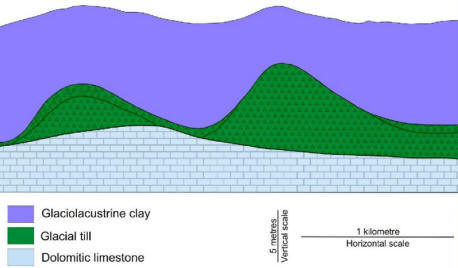 Image 28
|
 Image 29 |
 Image 30 |
 Back to Surficial Geology Compilation Map Series of Manitoba (SGCMS)
Back to Surficial Geology Compilation Map Series of Manitoba (SGCMS)


